Normal Histology Of the Breast
Robbie Wilson
01/12/06
Reception
The are a number of breast specimens which are received at a standard Histology laboratory, from Lumpectomy and mastectomy samples from theater to Core biopsies from the Breast Screening Unit.
On Reception at the laboratory all patient details are checked and the specimens divided into subgroups for different categories of dissection. At Antrim Area Hospital they perform BMS dissection, up to category C.
The specimen should be received fixed in 10% buffered formalin, but fresh specimens may be sent for Fresh/Frozen sections. This is a rapid process for quick results.
Also Sentinel Nodes may be sent unfixed for biopsy imprints with the Cytopathology Department.
Specimen Dissection
The next step is to dissect the breast specimen this is done following the standard operating procedures for each laboratory. The basic technique is to record a gross description of the specimen ie, size, appearance, weight, sings of disease etc. Then the specimen is dissected and tissue sections removed and placed into tissue cassettes. There will be a standard set of tissue blocks to remove but also any sign of disease seen on dissection will be removed and blocked. Also digital photography will be taken if the BMS or consultant sees fit.
Tissue Processing
At the end of each day the automated tissue processes are loaded with the tissue cassettes. The basic function of the tissue processor is to remove all water from the tissue and replace it with wax, they key is that is does not destroy the architecture of the tissue. This is preformed by washes in 70%, 90% and 100% alcohol, Xylene or Histo-Clear then Molten wax.
Once complete the cassettes are removed and the tissue blocks embedded in wax.
Microtomy
The first step is to remove excess wax by “trimming” the blocks, using a microtome that cuts thick sections.
The tissue blocks are then sectioned on the microtome resulting in sections generally 4 to 5 microns thick, the section and levels of sections which are taken are set out in the laboratories SOPs. These sections are then floated in a water bath and lifted onto glass slides.
Staining
Once completed the sections are now able to be stained, the stain that is used in Histology is an H&E stain, (Haematoxylin and Eosin). Haematoxylin stains the chromatin content of the nucleus (blue) and Eosin will stain the other components (pink).
The slides are then cleared and mounted for microscopic examination.
Special Techniques
Then reporting the specimen the consultant pathologist may request a range of different stains or methods, From imunohistochemistry for ER and Her/2 status, to PCR, FISH or special stains for different cellular components.
Histology of the Breast
Figure One
High power magnification of a section of normal breast tissue. This is showing a duct with the lining of pseudostratified ductal cells, and then the myoepithelial cells that can contract with hormonal changes. It is also possible to see the collagen network, fibroblasts, and a small arteriole supplying the area with blood.

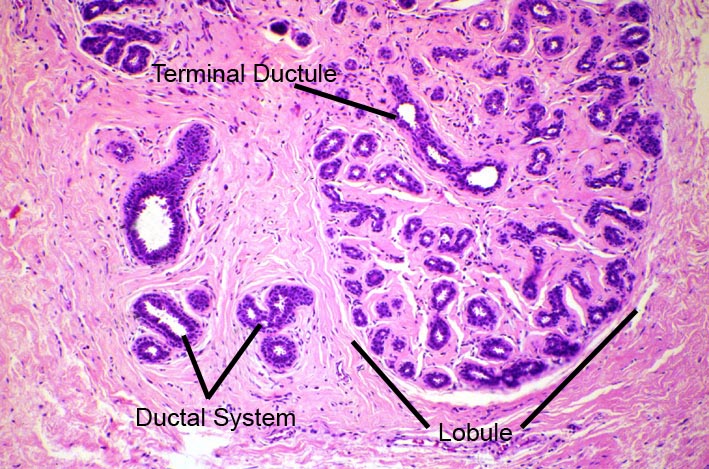
Figure Two
Low power magnification of a section of normal breast tissue. This shows a the lobule made up of terminal duct lobular units. Within the lobule it is possible to see a terminal ductile, also noted is the structures of the ductal system